(LỜI NÓI GIÁN TIẾP)
Lời nói gián tiếp (indirect/ reported speech) là lời tường thuật lại ý của người nói.
- Nếu động từ của mệnh đề chính ở thì simple present (say), present perfect (have/ has said) hoặc simple future (will say) thì trong lời trích dẫn ta chỉ đổi đại từ (pronouns) và chia động từ cho thích hợp với đại từ đó.
Ex: The farmer says, “I hope it will rain tomorrow.”
The farmer says that he hopes it will rain tomorrow. She has said, “I’m tired now.”
She has said that she is tired now.
- Nếu động từ trong mệnh đề chính ở thì simple past (said) thì trong lời trích dẫn ta phải đổi thì, đại từ
và một số từ hoặc cụm từ chỉ thời gian, nơi chốn.
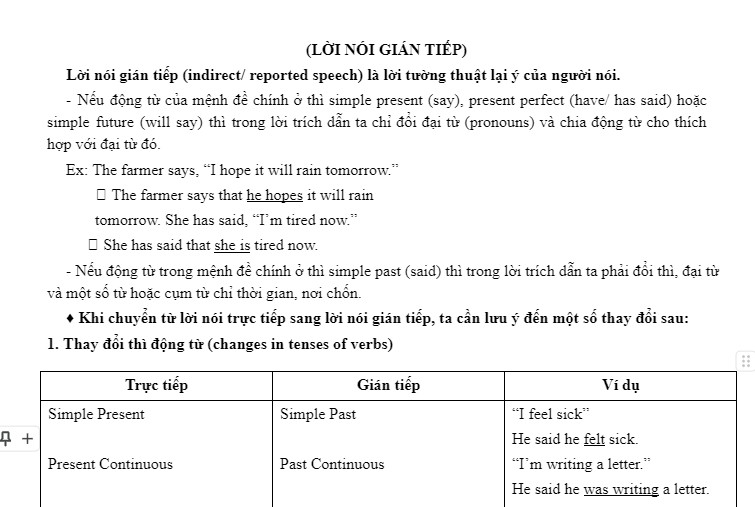
1. Thay đổi thì động từ (changes in tenses of verbs)
Trực tiếp | Gián tiếp | Ví dụ |
Simple Present | Simple Past | “I feel sick” |
He said he felt sick. | ||
Present Continuous | Past Continuous | “I’m writing a letter.” |
He said he was writing a letter. | ||
Simple Past | Past Perfect | “I arrived at 5p.m.” |
He said he had arrived at 5p.m. | ||
Present Perfect | Past Perfect. | “I have seen that film.” |
He said he had seen that film. | ||
Past Continuous/ | Past Perfect Cont. | “I was living in Viene then” |
Perfect Continuous | He said he had been living in Vien then. | |
Simple Future | Future in the Past | “I shall go to Japan in July.” |
He said he would go to Japan in July. |
- Ta có thể dùng thì simple present thay vì simple past trong lời nói gián tiếp khi diễn tả một thói quen hay một chân lý.
Ex: “I work late every evening.” He said he works/ worked late every evening. “The sun rises in the East.” The teacher said the sun rises/ rose in the East.
- Đối với các động từ khiếm khuyết (modal verbs) không có dạng quá khứ, ta có thể mượn các động từ
có cùng nghĩa.
must had to/ would have to
must not was/ were not to
can could/ be able to
may might
will/ shall would/ should/ be going to
Trực tiếp | Gián tiếp | Ví dụ |
This | That Those There Then That day The day before The previous day The day after The following day Before
The week after The following week | “I need this book.” He said he needed that book. “I’ll take these with me.” He said he would take those with him. “I’ll return here at 3 o’clock.” He said he would return there... “I’m going now.” He said he was going then. “I’ll do it today” He said he would do it that day. “I was in Hue yesterday” He said he had been in Hue the day before. “We’ll wait until tomorrow.” They said they would wait until the day after. “I was in Dalat three weeks ago.” He said he had been in Dalat three weeks before. “I’ll come to see her next week.” He said he would come to see her the week after. |
These | ||
Here | ||
Now | ||
Today | ||
Yesterday | ||
Tomorrow | ||
Ago | ||
Next week |
■ Cách đổi câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp
Câu mệnh lệnh, yêu cầu, đề nghị được đổi từ trực tiếp sang gián tiếp thường được mở đầu bằng những động từ như: order; command, tell, ask, request, ...và theo sau là tân ngữ trực tiếp chỉ người nhận lệnh + động từ nguyên mẫu (object + to-infinitive).
Ex: “Hurry up, Lan.” He told Lan to hurry up.
“Shut the door.” He ordered them to shut the door.
“Don’t leave the room.” He ordered them not to leave the room. “Please don’t tell anybody what happened.”
She ask me not to tell anybody what (had) happened.
Có hai loại câu hỏi: Câu hỏi Yes - No và câu hỏi Wh-
- Trong lời nói gián tiếp loại câu hỏi này được mở đầu bằng các động từ ask, inquire, wonder; want to know,...
- Dùng if hoặc whether ngay sau động từ giới thiệu của mệnh đề chính.
- Đổi trật tự câu hỏi thành câu trần thuật và đổi các đại từ, tính từ, thì của động từ,...
Ex: “Have you seen that film?” He asked if/ whether she had seen that film.
“Will Tom be here tomorrow?” She wondered if/ whether Tom would be there the day after.
2. Câu hỏi Wh- (WH – Questions: mở đầu bằng các nghi vấn từ như who, what, where, when,. )
- Trong lời nói gián tiếp loại câu hỏi này được mở đầu bằng các động từ ask, require, wonder, want to know, ....
- Lặp lại từ để hỏi (what, when, where,. ) sau động từ giới thiệu.
- Đổi trật tự câu hỏi thành câu trần thuật và đổi các đại từ, tính từ, thì của động từ,...
Ex: “What time does the film begin?”
He wanted to know what time the film began. “What will happen if she can not find her passport?”
He wondered what would happen if she could not find her passport.
Trong trường hợp câu trực tiếp có cả câu trần thuật lẫn câu hỏi thì khi đổi sang câu gián tiếp, phần nào
vẫn cứ đổi theo phần ấy.
Ex: “I have left my watch at home. Can you tell me the time?”
He said that he had left his watch at home and asked me if I could tell him the time.
Câu cảm thán thường được thuật lại bằng động từ exclaim/ say that.
Ex: “What a lovely garden they have!”
He exclaimed/ said that what a lovely garden they had. “How hot it is!” He exclaimed/ said that how hot it was.
- Câu trần thuật được đổi từ trực tiếp sang gián tiếp thường được mở đầu bằng các động từ say, tell,....
to say (that) ... to say to somebody... to tell somebody...
- Đổi các đại từ nhân xưng, tính từ hoặc đại từ sở hữu sao cho tương ứng với chủ ngữ hoặc tân ngữ mệnh đề chính.
- Đổi thì của động từ thành thì quá khứ tương ứng.
- Đổi một số tính từ chỉ định và trạng từ hoặc cụm trạng từ chỉ thời gian, nơi chốn
Ex: “I saw her yesterday”
He said he had seen her the day before/ the previous day.
Khi đổi từ câu nói trực tiếp sang gián tiếp, ta không đổi thì trong mệnh đề phụ ở các trường hợp sau dù
mệnh đề chính ở thì quá khứ.
Ex: He said, “I was born in 1980”. He said that he was born in 1980.
Ex: He said, “If I were you, I wouldn’t come here.”
He said if he were me he wouldn’t come there.
Ex: Mary said, “I wish I were a boy”.
Mary said that she wished she were a boy.
4. Trong lời nói trực tiếp có: could would, should, might, used to, ought to, would rather, had better,...
Ex: Tom said to me, “You had better not contact her”.
Tome said to me I had better not contact her.
Ex: My teacher said, “The sun rises in the East”.
My teacher said the sun rises in the East.